Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting
Section below generally aids in debugging Hudi failures. Off the bat, the following metadata is added to every record to help triage issues easily using standard Hadoop SQL engines (Hive/PrestoDB/Spark)
- _hoodie_record_key - Treated as a primary key within each DFS partition, basis of all updates/inserts
- _hoodie_commit_time - Last commit that touched this record
- _hoodie_file_name - Actual file name containing the record (super useful to triage duplicates)
- _hoodie_partition_path - Path from basePath that identifies the partition containing this record
For performance related issues, please refer to the tuning guide
Missing records
Please check if there were any write errors using the admin commands above, during the window at which the record could have been written. If you do find errors, then the record was not actually written by Hudi, but handed back to the application to decide what to do with it.
Duplicates
First of all, please confirm if you do indeed have duplicates AFTER ensuring the query is accessing the Hudi table properly .
- If confirmed, please use the metadata fields above, to identify the physical files & partition files containing the records .
- If duplicates span files across partitionpath, then this means your application is generating different partitionPaths for same recordKey, Please fix your app
- if duplicates span multiple files within the same partitionpath, please engage with mailing list. This should not happen. You can use the
records deduplicatecommand to fix your data.
Spark failures
Typical upsert() DAG looks like below. Note that Hudi client also caches intermediate RDDs to intelligently profile workload and size files and spark parallelism. Also Spark UI shows sortByKey twice due to the probe job also being shown, nonetheless its just a single sort.
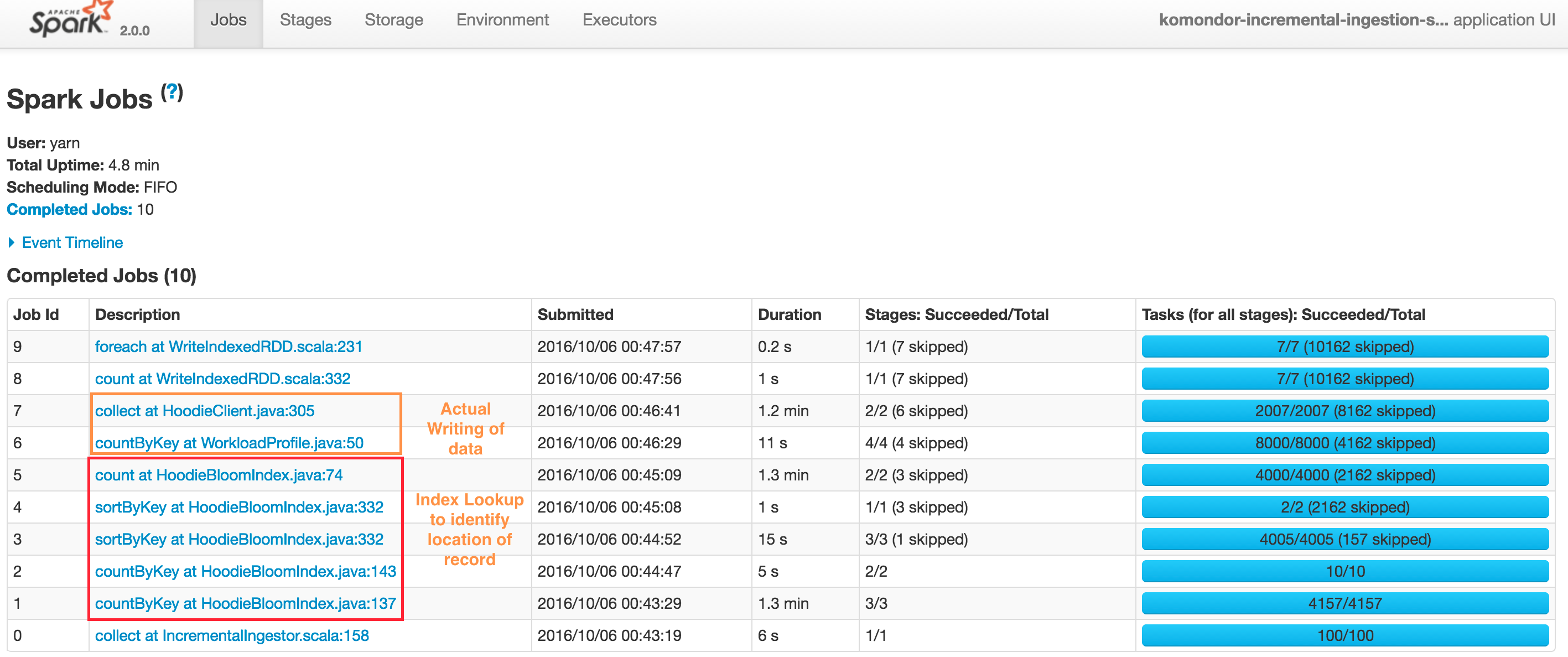
At a high level, there are two steps
Index Lookup to identify files to be changed
- Job 1 : Triggers the input data read, converts to HoodieRecord object and then stops at obtaining a spread of input records to target partition paths
- Job 2 : Load the set of file names which we need check against
- Job 3 & 4 : Actual lookup after smart sizing of spark join parallelism, by joining RDDs in 1 & 2 above
- Job 5 : Have a tagged RDD of recordKeys with locations
Performing the actual writing of data
- Job 6 : Lazy join of incoming records against recordKey, location to provide a final set of HoodieRecord which now contain the information about which file/partitionpath they are found at (or null if insert). Then also profile the workload again to determine sizing of files
- Job 7 : Actual writing of data (update + insert + insert turned to updates to maintain file size)
Depending on the exception source (Hudi/Spark), the above knowledge of the DAG can be used to pinpoint the actual issue. The most often encountered failures result from YARN/DFS temporary failures. In the future, a more sophisticated debug/management UI would be added to the project, that can help automate some of this debugging.